A Complete Manual for Flexible PCB Assembly
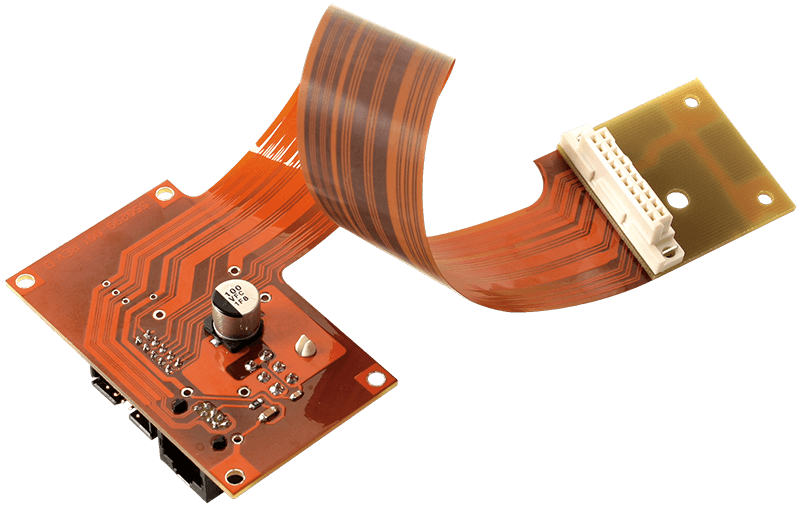
Table Of Contents
Can a printed circuit board be bent freely? Yes, but only in the case of flexible PCBs. You may wonder what the benefits of flexible PCBs are. Because they can adapt to any device with curved shapes, they provide unparalleled functionality and maximum versatility.
The electronics sector has seen exponential growth in flexible PCB assembly. Let’s get started as we examine its essential stages, benefits, difficulties, and new application trends in this post. Together, let’s explore this dynamic field.
1.What is a Flexible PCB?
Flex PCBs are also called Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs). Materials like polyester and polyimide are used to create flexible circuit boards. This is the perfect solution for compact and lightweight electronics that are space-constrained.
2.What is Flexible PCB Assembly?
Flexible printed circuit assembly, or Flexible PCBA Assembly, is the process of attaching components to flexible boards by using different techniques like polyimide base layers or polyester as substrate materials.
3.Flexible PCB Material
The structure of flexible PCBs is important. Insulating materials, copper foil, and adhesive are all used. Flexible insulating film is the most common material.
A FPC assembly’s foundation material might be either polyester or polyimide. Polyimide works well for reflow-soldering. For high temperatures, it is an excellent material. Copper layers can be laminated with base materials and circuit patterns etched on them. To protect the copper surface, the FPC surface is finished with a flexible polyimide mask or solder mask.

4.What are the advantages of Flex PCB Assembly?
(1) Superior Flexibility: Flexible PCB Assembly can be bent, folded, and twisted dynamically for reliable assembly. They can be adapted to complex 3D configurations.
(2) Lightweight Build: The flexible PCB Assembly is ultra-thin, lightweight and has a thin profile. This board is ideal for drones, wearables, and light sensors.
(3) Advanced Integration: Flexible PCBs are able to integrate high-density circuitry despite their compact size. They can include sensors, thermal layers, and antennas. They can be adapted to the device shape to optimize space for compact designs. It is possible to achieve “board as a system” solutions.
(4) Environmental Resilience and Longevity: Flexible PCB substrates are reliable across a wide temperature range. They are therefore suitable for precision industries. The protective layers protect against corrosion, moisture and dust. The service life is extended in harsh environments. The design is seamless, without moving parts. This ensures durability and repeatability.
5.The Key Steps of Flexible PCB Assembly

5.1 Fabrication of FPC
- Inspect unassembled boards: Check for defects on Flex PCBs that are not assembled.
- Verify fabrication precision – Ensure that flexible PCBs are manufactured according to the design specifications.
5.2 Component Preparation
- Compile your BOM: Compile a detailed Bill of Materials (BOM), specifying the components and their tolerances.
- Ensure compatibility: Ensure that all components are compatible with Flex PCB assembly.
- Pre-tin leads: To increase adhesion, solder the component leads.
5.3 Flexible PCB Baking
- Moisture Removal: Bake the flex-PCB stack to reduce moisture.
- Temperature control: Adjust the baking time/temp. based on PCB thickening.
5.4 Solder Paste Printing
- Precision application: To print solder paste, use a squeegee and a stencil that is oriented according to PCB layouts.
- Check consistency: Make sure that the paste is uniformly sized and aligned. This will prevent defects such as bridging and insufficient soldering.
- FPC Specific Requirements: For flexible substrates, choose thixotropic pastes that are optimized.
5.5 Silkscreen Printing (Optional).
- Mark test points, warnings, and components with insulation ink.
5.6 Component Mounting
- Automated placement: Use vision-guided pick and place machines to position components onto flex substrates.
- Self alignment: Use the self-aligning properties of reflow soldering to correct minor errors in placement.
- Prevention of defects: Hell for misplaced parts, tombstoning, or solder balls.
5.7 Reflow soldering
- Carrier Fixture:Flex PCBs should be secured during reflowing using high- temperature carriers with retractable pins.
- Optimized profiles: Adjust the heating zones according to the melting point of solder alloy.
- Gradual temperature changes: Avoid thermal shock by increasing temperatures slowly (=3degC/degC).

5.8 Thermal Lamination
- Layer bonding: Use heat/pressure lamination to apply additional layers such as coverlays and stiffeners.
5.9 Test
- AOI (Automated optical inspection): Uses cameras to detect misaligned parts, soldering bridges or missing components.
- X-ray Inspection: Automated X-ray inspection systems can be used to check for solder joints that are not filled properly or have voids.
- ICT (In-Circuit Test): Use bed-of-nail fixtures to verify electrical connectivity (like open, shorts).
- FCT (Functional test): Simulates real-world conditions in order to validate operational performance.
- Flying Probe Testing: For high-precision net tests on flex PCBs, use moving probes.
- Visual Inspection: Check for defects manually (cracks, delamination).
- Flex testing: Simulate bending cycles in order to test durability.

5.10 Post-Testing
- Singulate boards, perform final QC and then package compliant boards.
6.Flex PCB Assembly: Challenges and Opportunities
The following obstacles are faced by Flexible PCB Assembly despite its many advantages:
(1) Elevated Production Costs: Flexible PCB Assembly is made with premium materials and uses specialized processes. The cost of rigid PCBs is higher.
(2) Repair complexity: Complex component layouts, fragile substrates and dense components require special fixtures. Repairs become more difficult.
(3) Thermal Management Limitations: Flexible designs are limited in heat dissipation. Often, solutions like thermal vias or metal substrates are required to maximize cooling.
7.Flex PCB Assembly: Applications

Flex PCBA is a combination of electronic component integration and flexible circuit technology. It enables creative solutions across a range of sectors.
(1) Consumer Electronics
Wearable tech: Ultra-thin PCBs like smartwatches are powered by flex PCBs. They can be curved.
Foldable Devices: Flexible cables allow for seamless movement of foldable devices such as phones and tablets. They can be bent repeatedly.
Wireless Earbuds: Compact designs fit miniaturized flex-circuits while maintaining signal integrity.
(2) Medical Devices
Implantable Devices: Biocompatible PCBs can be found in glucose monitors and pacemakers. All of these devices require high reliability.
Surgical Tools: Flexible circuits are used in endoscopes and other laparoscopic tools to reduce their size and improve maneuverability.
Wearable Monitors: Flexible substrates are suitable for ECG patches, health sensors and wearable monitors. They are flexible and conform to the skin well for continuous monitoring.
(3) Automotive & Transportation
Sensors for ADAS: Flexible PCBs are used to connect LiDARs, radars, and cameras. They offer resistance to vibration under challenging conditions.
EV Battery Management: Battery packs with flexible circuits make the most of available space. They allow for efficient thermal management.
In-Cabin Electronics: Flex PCBs are used for ergonomics in In-Cabin Electronics. These designs are also space-saving.
(4) Aerospace & Defense
Satellites/Spacecraft: Lightweight flex PCBs reduce launch mass. They are also reliable in extreme conditions.
Military Electronics: Ruggedized Flexible Circuits are available from Military Electronics. They can withstand shocks, such as vibrations and temperature changes. Longer service life and better performance are made possible by this. These circuits are ideal for communication systems and drones.
(5) Industrial & Robotics
Robotic arms: Flexible joints allow for dynamic movement. They can be used to send electricity and signals.
Control Panels: Flexible PCBs for industrial machinery reduce maintenance and simplify wiring.
LED Lighting: Flexible strips that have integrated PCBs allow for curved, customizable lighting solutions.
(6)Emerging Technologies
Strain gauges incorporated in flexible PCBs, soft robotics, and electronic skin (eSkin) simulate human touch. It can be applied to delicate objects, robot grippers, and prostheses.
Flexible PCBs can be integrated with solar panels, energy storage and flexible PCBs for solar-powered wearables. They don’t shatter when bent.
Custom-shaped devices can be made by combining 3D-printed enclosures with a hybrid flex-rigid board. This is ideal for prototyping medical and aerospace products. This allows for shorter manufacturing lead times.
8.FAQs on Flex PCB Assembly
1) Solder paste requirements for flex PCBA?
It must be easy to apply. It should have good thixotropy and adhere well to flexible substrates.
2)What is the difference between a flex and a rigid assembly?
Flexible uses flexible substrates, special laminations and stress-relieving designs while rigid emphasizes stability.
3)What are the key design considerations for Flex PCB Assembly?
There are nine important factors. Material choice, location of bend radius components, trace route, mechanical anchoring, temperature control, tolerances, testing, and cost optimization.
4) What is the difference between Flex PCB assembly and manufacturing?
Manufacturing: Flex PCBs are produced as bare circuit carriers.
Assembly: Combine components to form functional electronic systems.
5) Is it possible to use through-hole technology in Flex PCB Assembly?
Yes, but requires careful design adjustments (e.g., stiffeners). Due to the flexing of flex materials, this is less common than SMT.
6) Is a conformal coat necessary for Flex PCB Assembly?
Although not universally recommended, it is highly recommended that flexible substrates be protected against environmental stress.
7) What are the Flex PCB Classifications?
Boards are usually classified as rigid-flex, multi-layer or double-sided.
8) Can flex PCBs be repaired?
You can replace the components on complex multi-layer boards by micro-soldering, but it is difficult.
9.Summary
The technology has been revolutionized by flexible PCBs. They can power anything from a foldable phone to life-saving devices. Their goal is to increase the intelligence and adaptability of electronics.
Contact Orinew if you need help with Flex PCB assembly or design.
Contact Us
Phone: +86-18123905375
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-18123905375
Wechat: +86-18123905375
Free Queto
Latest Blog
Table Of Contents
Contact Us
Phone: +86-18123905375
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-18123905375
Wechat: +86-18123905375
Free Queto



