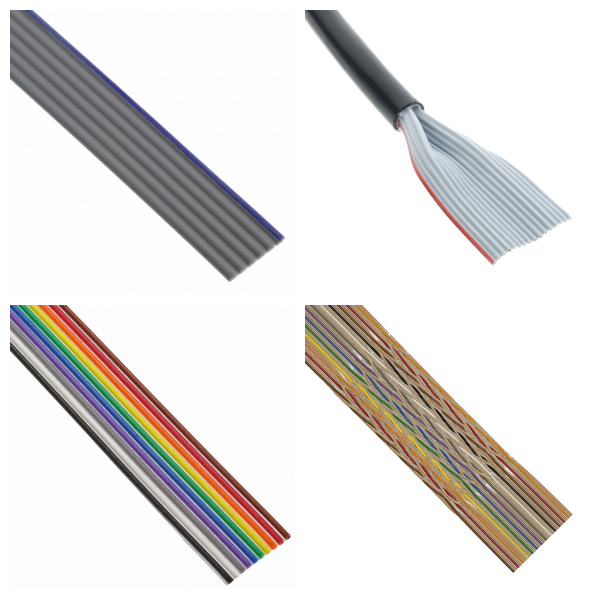
Flat Ribbon Cables
Flat Ribbon Cables have become a common wiring solution in industrial automation, electronic equipment, and other fields due to their compactness, flexibility, and reliability.
1. What are the Basic Structure of Flat Ribbon Cables?
Conductor: Usually composed of multiple parallel tinned soft copper wires, such as 7-stranded conductors, to improve conductivity and flexibility.
Insulation Layer: Made of materials such as soft PVC or FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene), it is heat-resistant and oil-resistant, and can maintain the integrity of the insulation layer when torn.
Band Form: The conductors are arranged side by side in a flat form to form a "ribbon" structure, and high-density connectors can be connected at both ends to save equipment space.
2. What are the Core Features of Flat Ribbon Cables?
High Flexibility: It can be easily bent and curled, suitable for scenes that require frequent movement such as robotic arms and robots.
Anti-interference: Through twisted conductors and shielding design, electromagnetic interference is reduced, suitable for signal transmission.
Environmental Resistance: Some models support oil resistance and high-temperature resistance (such as environments below 80 °C).
3. Where are Flat Ribbon Cables Used?
Internal Wiring of Electronic Equipment: such as computer wiring, signal, and power connection in industrial control equipment.
High-speed Motion Equipment: used for power or signal transmission modules that need to be frequently moved in automation equipment.
Oil-resistant Environment: scenarios that need to be exposed to oil in automobiles or industrial machinery.
4. What are the Differences Compared to FFC (Flexible Flat Cable)?
Structural Difference: Flat Ribbon Cables are usually a flat arrangement of independent wires, and the outer material is mostly PVC or FEP; while FFC is thinner, with integrated conductors on a flexible substrate (such as polyimide), suitable for high-density connections.
Termination Method: Flat Ribbon Cables are commonly terminated with standard IDC (insulation displacement connector); FFC mostly uses ZIF (zero insertion force) connectors.
Application Focus: Flat Ribbon Cables are more used for medium and low-speed signal or power transmission; FFC tends to be more high-frequency, high-density scenarios (such as inside mobile devices).
5. How to Choose Flat Ribbon Cables?
Conductor Quantity and Spacing: Select the number of conductors (such as 5 to 50 circuits) and spacing (such as 0.5mm and 1.0mm) according to the equipment requirements.
Environmental Adaptability: Parameters such as oil resistance and temperature resistance need to be considered.